At Tata Communications, climate change and environment protection are our key priorities. Therefore, we are focussed on creating a positive impact on the natural environment. We take proactive approaches to identify risks, and are continually working on programmes to conserve natural resources, and reduce emissions. We have a robust environmental management system, ensuring compliance with national and international standards, and our obligations towards all the stakeholders.

Climate change is one of the biggest global challenges to tackle. Protecting the natural environment from further deterioration and protecting our natural resources are still the most pressing needs. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) solutions offer a great opportunity to reduce global carbon emissions, and support the transition to a circular economy. Effective application of the Internet of Things (IoT), AI, and Machine Learning can be the best options for monitoring and mitigating the risk of climate change. As a digital ecosystem enabler, we will do everything we can to accelerate these processes and save resources. We are also promoting the use of renewable energy as a climate-conscious company. We have an environmental policy that works to develop services that are safe to use and harmless to the environment. Our efforts aim to minimise the use of energy and other resources, and enable the recycling or reuse of resources.
14
Major facilities in India are ISO 14001:2015 certified
As a continuous improvement plan, we have established an Environmental Management System (EMS) conforming to ISO 14001:2015. Our 14 facilities in India are certified in accordance with this standard. The implementation of the ISO 14001 standard helps us to regularly review the EMS, with programmes in place, to mitigate the identified environmental performance and impacts of our operational activities and services.
EMS also allows us to track our environmental goals, objectives, and training plan. EMS review and governance mechanisms include top management reviews (annual), reviews by management representatives and deputy management representatives (semi-annual), and regular reviews by corporate services (monthly). We also recognise the need to build proactive reporting and action mechanisms to address any potential environmental incidents, for which, we have developed an online environment incident reporting system for our employees and contract workforce. During the reporting period, no significant environmental incidents were reported. Further, no instance of non-compliance with environmental laws and regulations was reported for FY 2021-22.




Renewable Energy usage globally
Reduction in GHG emission intensity
Recycling rate of non-hazardous waste
Decrease in water consumption due to water conservation efforts and business continuity plans implementation
Energy conservation projects led to savings of
6.2 million kWhTowards positive climate action
The overall demand for energy in the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector is growing significantly. It is expected that the electricity demand for the IT sector will increase by 50% by 2030 and reach up to 3,200 TWh1 . Most of the energy consumption in the sector is due to powering servers, and significant indirect demand managing data centres. This will heavily contribute to the overall GHG emissions. Despite the significant impact, the ICT sector has the tremendous potential to reduce GHG emissions by 1.5 Gt CO2 by 20302.
At Tata Communications, we understand our critical role in driving energy and emission reductions, while creating substantial socio-economic value. Therefore, we are proactively working towards positive action plans on climate change issues. Reducing carbon emissions and responding to climate change have been our mission for over a decade, and our actions establish our position as an industry leader in addressing both, the risks and opportunities of the energy transition. In response, we have developed the climate change strategy, and are working towards the Net Zero emissions path, to reduce our environmental impact, and contribute toward climate action.

Climate strategy in action
Improving energy intensities for our facilities and data centres by pursuing continuous efficiency improvements
Improving our emission intensities through switching to renewable sources of energy or low-carbon energy
Developing low-carbon products and solutions for our customers
Decarbonising Scope 1 (Diesel based) emissions
Reduction in Employee and Business commute by introducing EV’s and other cleaner fuel options
Reduction in Upstream, Downstream and Supply Chain based emissions
Developing Carbon Community and Operational Offset programmes
Taking an active and constructive role in evolving climate change policy, solutions with governments, industry association and communities
Disclosure and Reporting
Our response to climate change
As a business, we are working towards a climate action strategy by improving upon the following priority areas:
1. Improving energy intensities for our facilities and data centres by pursuing continuous efficiency improvements
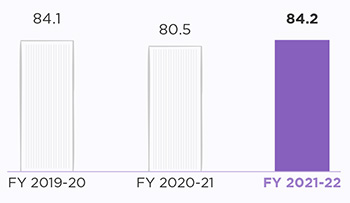
In FY 2021-22, we consumed 173 million kWh in our operations across the globe. Our energy intensity over the years has decreased to 84.20 (MWh per million-unit revenue in US$)6 as we have kept a keen focus on optimising our energy efficiency. We have expanded our focus towards optimising energy efficiency to continuously measure energy consumption, while also identifying the gaps in our operating procedures. This year, our Indian (facility infrastructure management) operations identified a total of 128 opportunities, involving projects related to heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC), switched-mode power supply (SMPS), and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) efficiency enhancement/ optimisation and consolidation, smart lighting (conversion of conventional lighting into LED), usage of IoT, and reduction in State Electricity Board (SEB) contract demand. Out of the 128 identified opportunities, 114 projects stand complete with a cumulative capital investment of US $1.2 million (INR 8.2 crore)3, resulting in cumulative energy savings of around 5.57 million kWh with cost savings of INR 4.8 crore (US $0.6 million). Further, our MAN and NLD teams completed 4 energy efficiency projects, resulting in energy savings of 39,200 KWH with cost savings of ~ 0.004 million US$ (INR 3 lakh). In addition to the projects, the team implemented the best practices, such as setting the air conditioner temperature to 24 degrees, setting SMPS in power-saving mode, and keeping grill tiles only in front of the Active Equipment Rack, resulting in savings of 593,126 kWh.
Energy intensity
reduced to
84.2 MWh
(per million-unit revenue in US$)
3Total 1.2 million USD were invested in FY 2021-22 which
included opportunities identified in the previous year
completed in the reporting year.
6 Revenue considered for calculations of Energy and GHG
intensity is US $2,054 million which excludes the subsidiaries
businesses of Tata Communications
Energy intensity (MWh per million-unit revenue in US$)
Our VSB Fort site in Mumbai has high-side equipment, which is managed by our FIM team. This site is a Tata Communication Limited owned premise that has a cable landing station, which is the most critical set-up. This station was managed using HT connection, which was then transformed to LT connection, using dry-type transformers. However, this conversion was associated with power loss and less capability. Therefore, only 5 out of 16 floors on the site were in operation.
To avoid these losses, we modulated the tap position of the HT transformer with optimised voltage between 400 to 415V AC LT. This initiative did not require any additional costs as it was executed by our in-house team.
The initiative was executed in August 2020, and since then we have saved an average of 5,018 kWh/month in FY 2021-22. This resulted in savings of 10.64 metric tonnes of carbon footprint in FY 2021-22. In addition, this has also led us to save INR 229,233 in FY 2021-22 without any investment.

We detected power transmission between the main LT panel and loads due to the low power factor at the load end, which is associated with 1% of the total transmission loss. Therefore, we focussed on correcting the power factor. We selected an inductive load and started an analysis from 8 October 2022 to 10 October 2022. Then we collected the energy loss from the IT panel to PAC, and calculated the loss due to low power factor with the help of a certified energy auditor. We then implemented the capacity bank, which resulted in decreased transmission losses, enhanced transition demand, and reduced operational cost. Energy savings of 10.5 kWh/day was recorded with this initiative.


At SLN Terminus Hyderabad
We decided to make the fifth floor at SLN Terminus Hyderabad operational as per business requirements. We observed that there are 100 conventional light fixtures installed that were more than six years old. These conventional lights consume more energy, deliver less illumination, and incur high repairing costs. We conducted a site survey to decide the appropriate LED fixtures for each type of old lighting fixture, without compromising on lux level and reducing the kWh consumption. Energy savings of 30,245 kWh per annum was recorded due to this initiative.
At VSB Delhi
We operationalised the fourth floor of VSB Delhi as per business requirements. We replaced 386 light fixtures, which were more than a decade old, with appropriate LEDs. This led us to reduce our energy consumption by 24,420 kWh per annumv.
VSB, and Ambattur, Chennai
At Ambattur, our existing common area lightings, such as streetlights, flood lights and post-top lanterns were fixed with CFL lamps, mercury vapour, sodium vapour, and metal halide lamps. This conventional lightning system was associated with higher energy consumption, lesser lifetime, poor illumination and safety concerns, and significant operational costs. We replaced these with LED lamps, and performed the same operation at VSB. These projects resulted in cost savings per annum of INR 2.64 lakh at VSB, and INR 1.08 lakh at Ambattur with energy savings of 2,268 kWh per annum.
2. Power Usage Effectiveness (PUE) enhancement
We are constantly updating our data centres with more efficient technologies to enhance the PUE value of our facilities to achieve the industry benchmark of 1.59.
1.7
Global average
PUE in FY 2021-22
Overall, the facilities infrastructure management (FIM) team in India manages 25 critical networks/business locations, where the average current PUE has improved from 1.8 to 1.6 since FY 2021-22.
Our international operations team also leads energy efficiency projects to achieve optimal PUE benchmarks for their regions. So far, these teams have achieved about a 1% power reduction as compared to last year. The average PUE for international data centres has improved to 1.8. Overall, our global average PUE stands at 1.7.
Thermal Optimisation Solution to improve the Power Utilisation Effectiveness (PUE): KIADB Bangalore
KIADB Bangalore is our critical International Transmission Management Centre (ITMC) that consists of 170 network server racks. PUE is the vital metric to assess the performance of network facilities from an energy efficiency perspective. In general, the PUE level between 1.51 to 2.0 comes under the average category. Our current PUE level is maintained at 1.57 level. We implemented a thermal optimisation project on a pilot basis/Proof of Concept (POC), to further enhance PUE from the ‘average’ category to the ‘efficient’ category of value between 1.2 to 1.5.
We installed 10 wireless temperature sensors in cold aisle containment. We also installed the ICOM controller and ICOM server to integrate between servers and sensors to record, command, and monitor the key performance parameters of the system.
The pilot project led us to reduce HVAC power consumption. In turn, our PUE level also improved from 1.56 (average category range) to 1.49 (efficient category range). The project resulted in annual power resource consumption of 161,280 kWh and 143 metric tonnes of CO2 emission reduced as a sustainability benefit. The project maintained a temperature gradient of 1 degree centigrade constantly, and also enhanced the system reliability due to adequate checks and controls.
At VSB Cochin
Our equipment room effectively operates at lower temperatures and lower PUE reflects the energy efficiency. However, the cooling system was problematic, in particular, the heat exchange system had issues. This faulty system resulted in the mixing of hot and cold air, increased PUE, and higher level of temperature in the equipment room.
We isolated the hot air area and used PVC curtains behind the racks. We also separated the unwanted cooling area with a PVC curtain and acrylic sheet. Then we called the OEM vendor for adjusting the set point according to the required air flow. We used existing energy metres for monitoring the energy consumption, with the support of energy auditors for finalising the idea, and then took the OEM vendor support to do the required setting in the cooling system.
These efforts resulted in improved PUE of the equipment area, increased the equipment efficiency, and reduced the operational cost.
This project, on average, led us to reduce our energy consumption by 152.5 KWH/day.

At VSB Chennai
VSB Chennai’s first floor block-1 CLS had 44 racks and only 11 were in operation. The racks occupied 2,512 square feet of area, but the operational racks occupied only 660 square feet. In addition, the faulty heat exchange system resulted in increased PUE and increased temperature in the occupied space. Therefore, we planned to implement cold aisle containments for the first floor TIC, CLS location. The budget of INR 369,568 excluding taxes was approved for this project. This project provided sufficient cooling for rack, minimised cold and hot air mixing at server hall, and improved PUE and achieved energy saving target of 7% against FY 2020-21 consumption. This project led us to reduce our energy consumption by 166 KWH/day.
3. Improving our emission intensities through switching to renewable sources of energy or low carbon energy
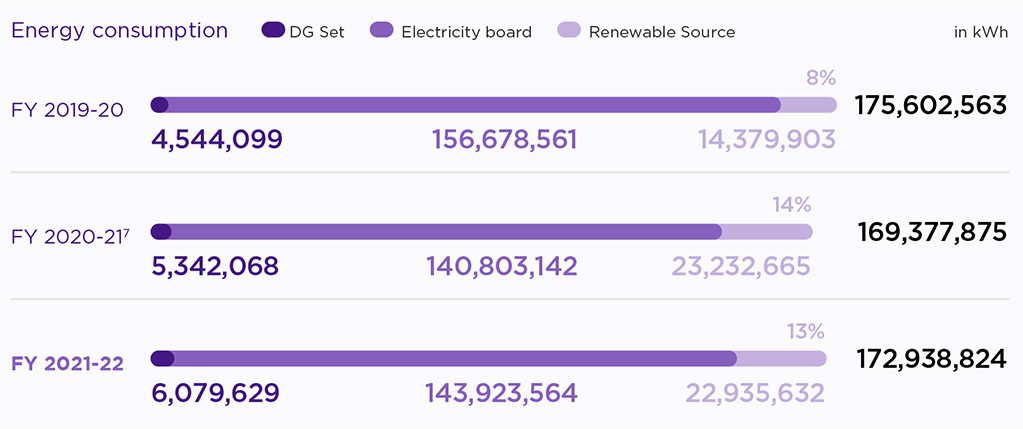
At Tata Communications, we consume nearly 173 million kWh of energy globally, mainly comprising indirect power supply (83%) from the national grid, while the rest comes from conventional sources and renewable energy sourced from third party/in-house. In our operations across the globe, almost 13% (~23 million units) of the electricity used in the reporting period was procured from either wind or solar energy. Out of this, 19 million units were sourced for Indian operations, while 4 million units were sourced for international operations.
13%
Of the electricity used
in FY 2021-22 came
from renewable sources
With an onsite installation capacity of 1.7 MWp and offsite capacity of 19.2 MWp, we are constantly exploring opportunities to increase our RE footprint. To meet the increasing energy demand for customer services as well as our facilities in India, on-site installation of 231 KWp capacity rooftop solar projects at VSB Hyderabad (129 KWp) and KIADB Bangalore (102 KWp) were completed, where power generation started from September 2021. Secondly, RE enhancement was done by partnering with STT GDC India at GK-1 Delhi. RE enhancement was completed in July 2021 from 49% to 60% by adding 0.25 MU annually. Additionally, RE power procurement for Dighi Pune (8.4 MU) and VSB Chennai (3 MU) has been signed off by the Board, and the delivery is expected to start in October 2022. Our facilities in Spain, Urduliz, and Derio have received a 100% Renewable Energy Guarantee of Origin certificate from the power distribution company. Further, to increase the RE percentage in the international operations, we are consulting experts to seek more avenues and opportunities to increase our RE footprint in facilities across the globe. In international operations, the RE composition has improved to 6% of the total energy consumption.

Reducing GHG emissions
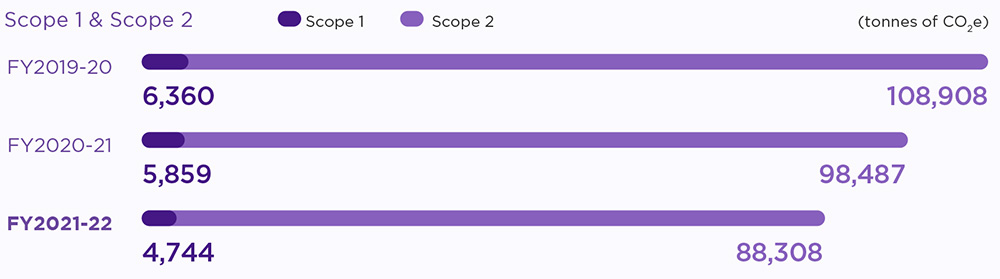
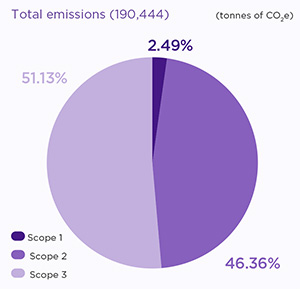
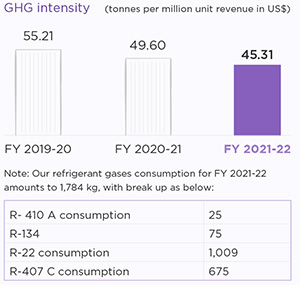
We understand the potential consequences of climate change caused by GHG emissions. Our operational carbon footprint is closely linked to energy consumption and the source of energy. We are continuously working towards reducing our carbon footprint at the operational level, and have significantly improved our GHG intensity to 45.31 (metric tonnes of CO2 per million US$ revenue8), a 9% improvement from FY 2020-21.
9%
Decrease in the emission intensity as compared to FY 2020-21
7The energy figures for FY 2020-21 have been reinstated based on the actual numbers after consolidation from regional teams.
8Revenue considered for calculations of Energy and GHG intensity is US $2,054 million which excludes the subsidiaries businesses of Tata Communications
We have an accounting mechanism to calculate our GHG emissions i.e., Scope 1 (emissions from DG sets, energy, and emissions from refrigerant gases, waste treatment in own facilities) and Scope 2 (emissions from purchased electricity) data, in accordance with the GHG Protocol Corporate Accounting and Reporting Standard.
For FY 2021-22, our Scope 3 emissions amount to 97,392 metric tonnes of CO2e* from business travel, employee commute, waste water, treated in municipal facilities, waste recycling, purchased and capital goods, downstream transportation and distribution, fuel related activities, and upstream leased assets.
 Source:
Source:
Scope 1 - arising from the consumption of fuels like diesel, the use of refrigerant gases and waste treatment inside the facilities
Scope 2 - Emissions from consumption of grid electricity

4. Developing products and solutions for our customers
We connect our business, the environment, and society through our innovative, low-carbon products and solutions. We develop and deliver green solutions that help our customers become more competitive and greener in their supply chains. We continue to provide and develop a variety of low-carbon products and services from our network, IoT, MES, cloud, and business collaboration streams to enable our customers to conserve energy and reduce GHG emissions.
This year, we assessed the carbon reduction offered by products and services deployed in FY 2020-21 and mapped with Tata Communications own operational GHG Emissions (Scope 1 and 2). The study confirmed that the potential GHG emission reductions through our Company’s low carbon products and solutions were around 661,543 metric tonnes of CO2e. This works out to an estimated carbon savings of six times the emissions produced by the operations of Tata Communications in FY 2020-21.

Carbon savings through IoT offerings
Our IoT ecosystem serves as a one-stop shop to provide IoT hardware, platform, application, and insights for the customer. This solution is upgrading a given city’s existing streetlights with smart streetlight solutions through automation of controls for energy and cost savings. This has resulted in additional energy savings of up to 20% and reduction of fault monitoring cost by 80%. It also ensures the right illumination on the streets for safe commuting. The overlay of the smart streetlighting solutions on LoRaWANTM connectivity enables a city to significantly reduce its carbon footprint, and help in transforming it into an intelligent and energy-efficient township, opening the avenue for a large number of smart city solutions to be enabled in the future, charting the path for other cities to replicate.
6:1
Carbon emissions saved for customers as compared to our Company’s operational emissions in FY 2020-21
Low-carbon products and solutions table
| Products and solutions | Types of environmental savings | |
|---|---|---|
| IoT | Smart streetlight |
|
| Smart utility metre | ||
| Smart energy monitoring | ||
| Mobility and MOVE | Transport and logistics |
|
| Aviation | ||
| Telematics | ||
| Unified communications | CISCO – video as a service (VaaS) | Avoidance of travel – instant, efficient and hasslefree video collaboration reduced in-person meetings |
| CISCO powered solution – UcaaS | ||
| Voice solution | ||
| Cloud and managed hosting | Remote working solution |
|
| Managed cloud services | ||
| Media and entertainment services | Remote production solution |
Fuel savings – avoidance of travel; instant, efficient and hassle-free video collaboration reduced in-person meetings |
| Managed cloud services | ||
5. Decarbonising diesel-based Scope 1 emissions
Currently, we are using diesel generators as backup power for the facilities to provide continuous energy in case of grid energy outages leading to diesel-based emissions. As we advance towards aggressive climate actions, we understand that, though relatively low, diesel-based Scope 1 emissions also need to be eliminated and contribute to the decarbonisation plans of the Company. Moving forward, we are exploring such avenues which would not only eliminate these emissions but also provide a better energy-efficient source for operating facilities and supporting infrastructure. To support this ambition, we are looking into Battery Energy Storage Systems to not only provide an efficient system, but also enable storage of grid energy onsite to eliminate diesel use, thereby leading to the elimination of emissions.
6. Introducing EVs and other cleaner fuel options
The services we provide to our customers require our employees to travel to various locations. Therefore, to enable business travel, our Company provides hired vehicles for employees for business purposes. Additionally, for employee commuting, we also provide third-party vehicles. Currently, the vehicles are diesel-based, which contribute towards Scope 3 emissions of our Company. We are exploring cleaner options, such as EVs, CNG-based vehicles, etc. for our fleet, and are working towards the installation of charging stations. This would also encourage the employees to use cleaner fuels, leading to an overall contribution to our climate action.
7. Reduction in upstream, downstream and supply chain-based emissions
Based on our Scope 3 emissions accounting, we recognise that supplier-based emissions are one of the significant ones in the Scope 3 categories. We have identified our top suppliers (60% of the procurement amount), and their key initiatives and emissions towards climate change. To reduce such emissions, in addition to Sustainable Supply Chain Framework, we are exploring engagement opportunities with our suppliers through campaigns to educate them on climate change and impact mitigation, influence to respond to CDP annually, encourage innovation to reduce climate impacts, and collaborate with suppliers on innovations to contribute to net-zero goal.

8. Developing community carbon offset programmes
To meet the twin objective of climate action and creating a positive impact on the communities, we are working on carbon offset projects. To initiate the projects, a thorough feasibility analysis was conducted in FY 2021-22, including baseline and community-need assessment. Based on such assessment, projects, namely: smart cookstoves in Jharkhand, Orissa, and Meghalaya, and plantation projects in Maharashtra, have been identified and undergone both, financial and operational validation. The implementation and registration under Gold Standards and VCS registry will be completed in FY 2022- 23. These identified projects are expected to expand in scale till FY 2029-30 with the potential to offset around 41,000 tonnes of CO2 in FY 2029-30.
9. Working towards evolving climate change policy and solutions
We are working to improve our advocacy relations to overcome regulatory and institutional challenges, especially on the RE front. With roadmaps envisioned by the teams on climate action, we have a lot of initiatives in the pipeline, for which, we are actively seeking partnerships and expert opinions. These interventions will help build the capacity of the internal teams, resulting in the expansion of our climate action.
10. Disclosure and reporting
Being a climate-focussed company, we realise the importance of transparent and voluntary disclosures, and reporting of our climate response, which are a testimony to our work, and demonstrate our commitment and leadership to all our stakeholders. The various forums and frameworks according to which we disclose our climate performance are: Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), International Integrated Reporting Framework (IIRF), Business Responsibility and Sustainability Report (BRSR), Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), and EcoVadis. Since these are public disclosures, we communicate our performance in a more transparent way, which always makes the information accessible to our stakeholders.