At Tata Communications, we leverage our expertise as a digital ecosystem enabler to unlock the potential and opportunities that the disruptive force of technology offers to society. By connecting people and delivering meaningful and sustainable social impact through our targeted CSR initiatives, we are empowering under-privileged communities through our community-engagement opportunities.





We recognise our responsibility to leverage our scale and expertise to deliver positive change. We engage with local groups and associations to implement targeted programmes that focus on promoting good health, quality education, sustainable livelihoods and employability. Our CSR policy has been formalised as per the requirements of Section 135 of the Companies Act 2013 and derives inspiration from Tata group’s philosophy ‘to improve the quality of life of the communities we serve globally through long term stakeholder value creation based on leadership with trust’.
We have adopted the Tata Affirmative Action Programme (TAAP), a Tata group level initiative which aims to address structural and social inequities in India by providing equal opportunities and inclusive growth to historically marginalised social groups, namely the Dalits and Tribals. We have aligned our CSR initiatives with the UN SDGs, prioritising five SDGs (SDGs 3,4,8,10 and 17) which we promote through our social impact programmes. Our programmes are designed to improve the capabilities, quality of life of underserved sections of the community, particularly women, young girls and youth.
FY 2020-21 highlights
31,000+
Volunteering hours

430,973
Number of people benefited
US$ 1.59 mn
CSR spend (INR 11.84 crore)

66,600+
COVID-19 relief beneficiaries

100%
Need and impact assessment of community projects

CSR at Tata Communications is directed by the CSR Committee, which oversees the Company’s social responsibilities. The Committee engages in periodic reviews on policy objectives, while also offering guidance on enhancing the scale, quality and impact of the programmes. Additionally, the Company’s Global Management Committee (GMC) takes complete ownership of all CSR interventions and offers guidance on how to improve impact on ground. CSR forms part of the quarterly report to the CEO, who also reviews and guides CSR from time to time. Furthermore, the function head conducts annual reviews of all CSR projects in conjunction with the project partner. These reviews entail in-depth discussion of deliverables, milestones achieved, challenges, budget utilization and way forward.
 To know more about CSR committee,
please refer to the Annual Report 2020-21
To know more about CSR committee,
please refer to the Annual Report 2020-21

Our CSR projects are underpinned by robust monitoring and evaluating mechanisms. Our regular M&E efforts include, conducting governance calls (weekly, monthly and quarterly) with project partners, sharing of utilisation certificates, progress and annual project reports by NGO partners.
All our projects get evaluated by independent agencies for detailed impact assessments to ensure that they are relevant and responsive to the needs of the communities and document best practices. This year, we conducted an independent impact assessment on one of our education projects - ‘A New Education Worldview (ANEW)’. ANEW facilitates holistic school reformation in 110 government schools across Gurugram District (Haryana) by equipping teachers with evolved teaching practices, integrating technology into the curriculum of first-generation learners, improving learning levels of students, reducing dropout rates, and enhancing community ownership. The study adopted Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development’s (OECD) Development Assistance Committee (DAC) framework and mixed methods approach to understanding the relevance, effectiveness and impact of the programme both quantitatively and qualitatively.
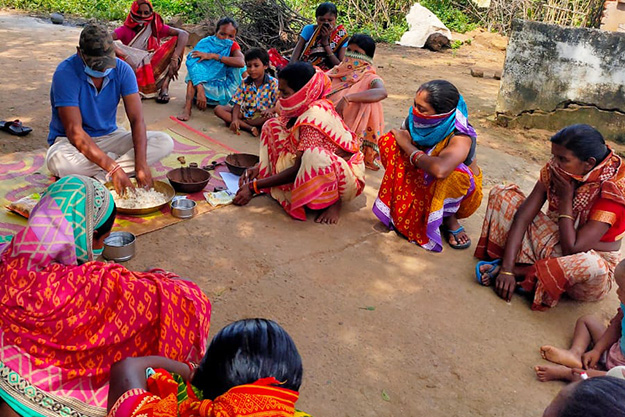


Tata Affirmative Action Programme
In FY 2020-21, 51% of the total CSR budget
– US$ 0.80 million (INR 6 crore) was spent
on Affirmative Action projects.
Of the 17 projects in India being supported
under CSR, two projects are 100% AA,
two have significant AA focus
(70-90%
or more) and seven have partial AA focus
(less than 70%).
51%
of total CSR budget for FY 2020-21 was spent on Affirmative Action projects
The five SDGs we have decided to champion provide an overarching framework to our global CSR mission across three priority areas: Education, Employability and Sustainable Livelihoods and Healthcare.
Projects
We are currently implementing 17 projects
across the three priority areas enumerated
above. We implement community projects in
partnership with different NGO partners while
supervising, monitoring interventions, and
addressing challenges. Our formal grievance
process is through an online form available
in the Sustainability section (community
sub‑section) of the Tata Communications
website. This helps in better tracking through
recording and resolving grievances.

Education
We seek to transform the education system
using digital enablement, educators’
empowerment and youth engagement to
create exponential social, economic and
environmental impact.
CSR Investment: US$ 0.53 mn (INR 3.96 crore)
Lives touched: 37,872
Employability and Sustainable Livelihoods
Empowering youth and women with relevant skills and enabling them to be industry-ready by equipping them with the right attitude and values to enhance their living conditions and contribute actively to the economy. Training youth for the telecom sector is a prime focus area.
CSR Investment: US$ 0.86 mn (INR 6.40 crore)
Lives touched: 101,592
Healthcare
Ensuring access to healthcare to underserved communities especially adolescents, women, children and the elderly. Facilitating collaborative basic, translational and research in healthcare and promoting mobile health services.
CSR Investment: US$ 1.1 mn* (INR 8.20 crore)
Lives touched: 30,245
*Note: National Cancer Grid (year of initiation and funds disbursement-2016) – INR 2.5 crore, Assam Cancer Grid (2018)- INR 5 crore and Dhristi (2020)- 70.15 lakh
Employee volunteering

The Global Employee Volunteering Program (GEVP) at Tata Communications was formally initiated in 2017 which is a key pillar of our culture. The GEVP motto – for a better world and workplace – requires the 12,500 strong workforces from 40 nationalities to go ‘beyond business’ and contribute to the social advancement of communities.
The new way of volunteering
And what rose from the crisis was a new
volunteering strategy and the launch of the
very first virtual volunteering campaign in
May 2020. The campaign invited employees
to step up and volunteer their time and skills
during COVID-19 to reach out to people and
communities in the hour of the crisis.
Working with our volunteering partner, Goodera, we curated completely virtual activities, that did not require the volunteers to step out during the pandemic. The objective was to create meaningful volunteering experiences despite the changed scenario. The unchanging COVID-19 situation made it clear that virtual volunteering was no longer a stop-gap solution but a new way of volunteering.
Collaboration
During Tata Volunteering Week 14, in
September, we extended our volunteering
initiatives to other Tata Group companies.
Around 400 employees from 12 group
companies participated in various
activities, amongst them Tata Chemicals,
Tata Steel, Tata Power, Starbucks, Croma,
Air Asia, Tata Coffee, Tata Power Delhi
Distribution Limited, Tata Consulting
Engineers Limited, Voltas Limited,
Amalgamated Plantations being some of
the companies.
4th edition of DRIVE WEEK, a one of its kind global volunteering campaign for community action organised virtually for the very first time to unite all the on‑roll employees to volunteer for a cause of their choice for a better world and workplace.
During the reporting period, we have had 133 volunteering events, resulting in 31,013volunteering hours contributed by 7,572 volunteers with a per capita average of 3 hours per volunteer

From offering children scholarships to building the capacity of the teachers, and engaging with them, we endeavour to promote access to quality education while encouraging life‑long learning. We are working with our non-profit partners to help create sustainable and inclusive technology-based solutions in Haryana, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu across 136 schools and 7 colleges.
Key initiatives
17
Community learning centers
As many as 17 community learning centres have been set up at venues granted by local village councils to extend regular learning support and mentorship to children while giving them a safe space where they can express their thoughts and interact with other children. The emphasis on technology-enabled learning is intended to improve the quality of learning and, thereby, enhance student experience along with improving student learning outcomes. An inter-linked objective is to familiarise young learners from resourcepoor backgrounds with digital developments to inspire confidence and a sense of comfort in using technology.

International CSR activities
Tata Communications has expanded its CSR
footprint globally. The international CSR
activity is over and above the requirements of
the Companies Act, 2013.
Tata Communications have been working with the Evergreen Secondary School through the ‘Network for Teaching Entrepreneurship (NFTE)’ programme in association with Halogen Foundation, Singapore. It was initiated in 2016, with the desire to help resolve some of the fundamental concerns of the community we serve, by empowering youth with the relevant skills that will allow them to be industry-ready, as well as have the right attitude and values to enhance their future prospects.
NFTE programme annually benefits 37 students. The programme targets students of socio-economically underserved background to instil an entrepreneurial mindset through experiential activities, regular work sessions with corporate volunteers and various other activities. The programme has helped them to move out of their current situations by improving their social mobility, self-esteem and skills in Mathematics and English.
Schools in action for the planet

Environment-focused education
Tata Communications partnered with
Auroville Foundation to implement a
robust education programme to create
future leaders who are ecologically
aware and are attentive to the principles
of sustainability. The project equips
school going children with the right
knowledge and skillsets required to
become solution-oriented stakeholders
of their local environments. Launched
in March 2020, the project was adapted
for delivery through online format,
following the mobility restrictions
induced by COVID-19.
Adopted methodology
The online modules make young
learners aware of the complex
interconnections in the natural world,
by enabling learners to engage with
environment through a range of
interactive hands-on methods. The
education modules are designed to
make space for mutual appreciation,
intellectual and mental growth and
facilitate engagements with family
members and neighbours.
Skits: The skits delivered information on topics such as organic farming and solid waste management along with humour and hyperbole to make it more accessible and relatable. Each skit was followed by a Q&A session and a discussion to assess and further facilitate the understanding of the topic introduced.
Online games and puzzles: Games such as Scavenger hunt (used to help learners know more about plastics) and puzzles (such as putting pictures together to know more about an insect, bird or an animal) were followed by a summation which brought together all the individual learnings.
Bamboozle: A rapid hunt where children fetched different items displayed on the screen. The primary objective was to point out how many of those items were in fact made out of plastic.
Quiz: Different forms of quizzes were used to help the children take ownership of their learning and to display their comprehension of it. The modules were also designed to foster an atmosphere of trust, co-learning and collaboration. They were structured as spaces where the students felt the freedom for self-expression without being judged and where they received appreciation for their contributions, skills and abilities.
Outcome
We drive sustainable livelihood generation with a belief that a society of empowered individuals who enjoy a decent standard of living, can create overall prosperity and help develop a nation.
Initiatives under the umbrella include:
1
Employability
2
Sustainable Livelihoods
Employability Highlights
(>5,300 women) imparted vocational skills
trained in nine batches of Women Entrepreneurship Development Programmes (WEDP), post-training one-year assistance helped them to leading to the formation of 58 enterprises from the batches of WEDP in FY 2019-20
sensitised through ten entreprenership awareness camps
adult learners gainfully employed after training with an annual average salary of ~US$ 1,875 (INR 139,200)
of adults in income-generating activities
Lakhpati Kisan - Smart Villages

Creating their own fortunes
One of our flagship projects that is
implemented in partnership with Collectives
for Integrated Livelihoods Initiatives (CInI)
in the only tribal-majority (>60%) district in
Maharashtra with an extremely low Human
Development Index value. This holistic
intervention is enabling 7,500+ tribal women
farmers (98% tribal households, 45,000+
beneficiaries) in 41 villages in Dhadgaon block
of Nandurbar, Maharashtra to craft their way
out of poverty and enhance their quality of life
and life choices.
Adopted methodology
Water conservation and irrigation
development: Restoration of traditional
water harvesting structures, building lowland
group wells (17), deepening existing wells
(02) to share resources between farmers.
Additionally, lift irrigation performed seven
times through the year in places where check
dams may not be feasible.
Agricultural cluster development: Promotion of climate-smart technologies like drip and mulch-based precision farming for high-value agricultural produce along with encouraging diversification of crops. Setup 7 high-tech nurseries producing 1.4 mn+ disease-free sampling, hence generating an average annual income of US$ 2,260 (INR 167, 860) for 1,680 families.
Livestock development: Promotion for income diversification amongst farmers living in uphill villages with lesser avenues of income generation, the component focuses on introducing quality bucks, increasing the herd size of farmers, improving feed sources, bettering goat management practices and introducing paid, shared veterinary management support.
Digital inclusion initiatives: Improving literacy through an integrated approach to technology in education, awareness of and access to health-related government schemes (particularly for pregnant and new mothers along with children) through a community-based nutrition initiative and making safe drinking water available for all by strengthening sources and enhancing access to potable drinking water through paid, shared drinking water stations.
Trainings: Conducting regular agricultural -training and veterinary camps to build capacity and awareness of farmers on improved agriculture and livestock management practices. Skilled manpower for advanced agriculture practices by conducting three training sessions on leadership for Farmer Producer Company, 100 training sessions on livestock management practices, 136 training sessions on high-value farming, 11 training sessions for Village Institution’s members, six pre-season training for community resource persons
Outcomes
Our key focus is improving access to quality healthcare services for people belonging to the underserved sections of the society, with emphasis on prevention and care of non-communicable diseases in rural areas.
Assam Cancer Care Programme
We focus on reducing the disease burden
of cancer in rural Assam by facilitating early
diagnosis. Through the installation of scanners,
we are promoting the ‘telepathology’
infrastructure for diagnostics in cancer care
in remote locations of Assam. This would
enable pathologists to view and report the
cancer stage in a timely manner and reduce
travel time for patients from remote areas to
bigger hospitals in other cities for preliminary
consultation.
National Cancer Grid
The project aims to bridge the training gap
observed among healthcare workers in the
cancer screening programme and improve the
effectiveness of the cervical cancer screening
programme across India. Introduction of
patient navigators in the project hospitals to
assist patients’ access to hospital facilities
Drishti

Implementing a larger vision
Launched in 2020, Drishti is our first
initiative in the state of Bihar which has
the lowest Human Development Index
(HDI) value amongst all the states of
India. For Drishti, we partnered with the
Akhand Jyoti Eye Hospital to support their
ambitious goal of eradicating bilateral
blindness in Bihar through employmentlinked
education and preventive eye care.
Adopted methodology
Developing leaders: E-MBA and advanced
leadership training sessions, including
soft skills along with aptitude-specific
skills training for senior resident girls to
prepare them for leadership positions in
the eye hospital.
Technology for healthcare: Development of a data-capturing smart phone and integrated web application to centrally store and digitally capture patient data from screening initiatives.
Healthy and productive lives: Vision screening for 50,000 young learners in government run schools/anganwadi centres to address vision loss in childhood. Identified children in need of spectacles or corrective eye surgeries are provided the same free-of-cost.
Enabling young girls: Employment and life-skills linked residential education to 50 underserved young girls from rural Bihar to develop them as future leaders and change makers in the domain of eye care. A blended programme of classroom trainings, use of IT platform and exposure to leadership and prepares participants to undertake professional study in optometry. The initiative creates shared value as upon successful completion of professional studies, these girls are absorbed and deployed into the hospital system where they earn stable livelihoods while contributing to the larger goal of blindness eradication.
Outcomes
The onset of COVID-19 in 2020 affected the larger rollout of this initiative.
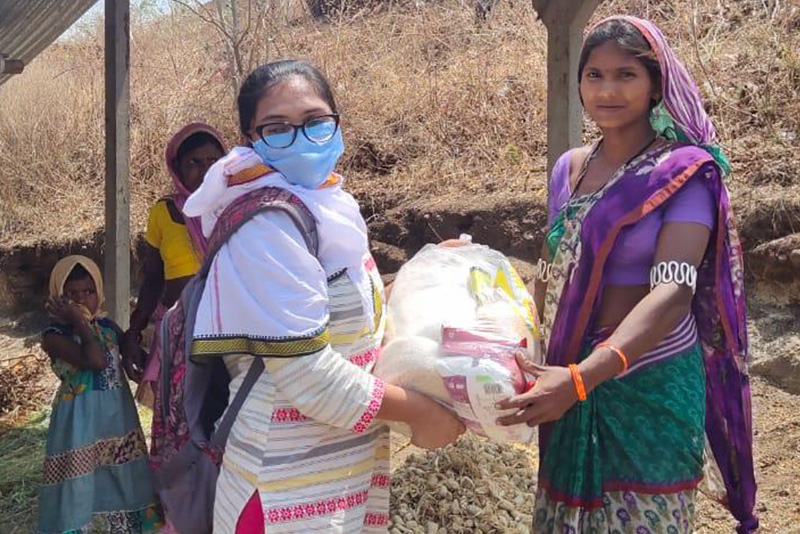
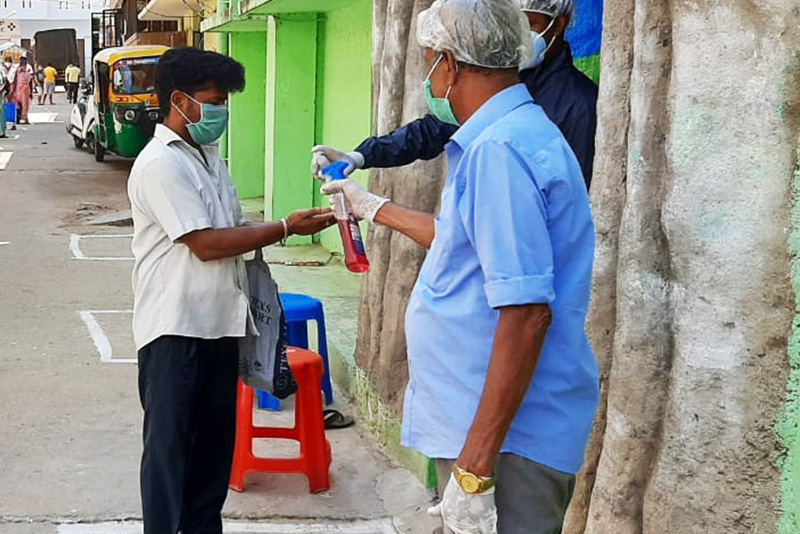
Our efforts in the context of COVID-19 were guided by a response framework aimed at leveraging our strengths to support communities under three significant areas: extending digital infrastructure support, bolstering healthcare services and providing relief.
Key activities
1
Partnered with Tata Power Delhi Distribution
Limited (TP-DDL)
to provide ration kits and hygiene supplies to
1,000 underserved families from the Jhuggi-
Jhopri (JJ) cluster in Delhi; Moreover, 55
underprivileged women were supported to
gain livelihood through mask-making which
led to income generation during the
lockdown period.
2
US$ 30,424 (INR 22.59 lakh) contributed in
partnership with Tata Motors
to support the impacted, including migrant
workers, nomadic tribes, health workers,
through Sumant Moolgaokar Development
Foundation (SMDF) in Pimpri Chinchwad
Municipal Corporation (PCMC) area,
Pune, Maharashtra.
3
Initiated a global employee donation
with a dollar-to-dollar match by the Company;
contributed more than US$ 102,357 (INR 76
lakh) to Tata Community Initiative Trusts
towards supporting distressed families.
4
Distributed 6,500 handmade masks
to communities located in Bhosari,
Panchasheel Nagar, Vaiduwadi, Malwadi at
Pune; women supported to gain livelihood
through mask-making.
5
Ensured the well-being of communities
by extending our support to four of our
long-term partners in Haryana (1,000+
beneficiaries), Mumbai (500 students and
their families for 15 days) and Bengaluru
(1,500 students and their families) during
the pandemic.
6
Distributed dry ration
to 1,100 families of migrant labours at
Nandurbar, Maharashtra.

